
The Assistant Professor Salary in India, especially in IITs and Universities, reflects the prestige and responsibilities associated with these roles. India is home to a vast network of higher educational institutions, ranging from world-renowned Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) to central and state universities. These institutions not only shape the academic landscape of the country but also provide excellent opportunities for career growth in teaching and research.India is home to a vast network of higher educational institutions, ranging from world-renowned Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) to central and state universities. These institutions not only shape the academic landscape of the country but also provide excellent opportunities for career growth in teaching and research.
Assistant Professors play a pivotal role in these institutions by imparting knowledge, mentoring students, and contributing to cutting-edge research. Their salaries, career progression, and benefits vary significantly based on the type of institution they serve in. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of Assistant Professor positions in IITs and Universities, exploring eligibility criteria, pay scales, perks, and career growth.
Higher education in India has witnessed remarkable growth over the years. The rise of IITs has symbolized technological and scientific advancement, while universities continue to nurture diverse academic disciplines. Both types of institutions cater to different aspirations—be it research-focused careers in IITs or teaching-oriented roles in universities.
This blog delves deeper into the structure and expectations of faculty positions at IITs and universities, equipping aspirants with the knowledge needed to make informed career decisions.
About IITs
Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) are premier autonomous public technical and research universities established to advance engineering, technology, and science education in India. The first IIT, IIT Kharagpur, was established in 1951, and it marked the beginning of a transformative journey in higher education. Today, there are 23 IITs across India, including IIT Bombay, IIT Delhi, IIT Madras, IIT Kanpur, IIT Roorkee, and IIT Guwahati, which are widely recognized for their excellence in academics, research, and innovation.
These institutes are centers of innovation, focusing extensively on cutting-edge technology development, fostering entrepreneurship, and promoting interdisciplinary research. IITs are highly competitive, with admissions based on the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE Advanced) for undergraduate programs and the Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) for postgraduate programs.
Globally, IITs are acknowledged for their contributions to science and technology, and several IIT graduates occupy leadership positions in multinational corporations, research organizations, and government agencies. Their international collaborations and partnerships with top universities worldwide make IITs hubs of advanced scientific inquiry and innovation.
With state-of-the-art infrastructure, IITs attract top-tier faculty and students, offering excellent opportunities for academic careers. Professors and researchers at IITs often lead groundbreaking research, secure patents, and receive funding from national and international organizations, further cementing their reputation as world-class institutions.
About Universities
Indian universities, including central, state, private, and deemed institutions, cater to a wide range of academic disciplines and research areas. They form the backbone of the higher education system in India, offering opportunities for undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral studies. Some of the most renowned central universities include Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Banaras Hindu University (BHU), University of Delhi (DU), and Hyderabad Central University (HCU). These institutions have gained national and international recognition for their excellence in teaching, research, and cultural diversity.
Universities in India are governed by the University Grants Commission (UGC), which regulates academic standards and frameworks. Pay structures in universities are standardized under the 7th Pay Commission, ensuring fair salaries and benefits for faculty members. Additionally, universities emphasize interdisciplinary studies, enabling students and researchers to explore various fields such as humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and professional courses.
Many universities focus on regional development, making higher education accessible to students from rural and remote areas. State universities, in particular, play a vital role in democratizing education, while private universities cater to modern demands by introducing industry-relevant courses and partnerships.
Central universities often act as research hubs, providing funding opportunities and collaborations with national and international organizations. They also host cultural festivals, academic conferences, and workshops, contributing to holistic academic and personal development.
Universities are ideal for those interested in teaching-oriented careers combined with research opportunities. Their flexible academic structures and regional presence make them attractive options for educators looking to make an impact on society while advancing their academic careers.
Assistant Professor Salary in IITs
1. Age, Education, and Eligibility
- Age Limit: Typically, candidates applying for assistant professor positions in IITs are below 35 years, although there is some relaxation for reserved categories.
- Educational Qualifications: Candidates must possess a Ph.D. in a relevant field with at least 60% marks at all degree levels. Additionally, postdoctoral experience and research publications in reputed journals are highly preferred.
- Additional Requirements: Strong research backgrounds, international conference presentations, and collaborations with reputed institutions add to a candidate’s profile.
- Important Note: CSIR NET or similar eligibility tests are not mandatory for IITs. The selection is primarily based on research credentials and interview performance.
2. Salary Structure
IITs follow a structured pay scale based on grades and experience. Salaries are highly competitive and designed to attract world-class talent in teaching and research. The pay scales are categorized into different levels based on qualifications and years of experience. Newly appointed Assistant Professors typically start at Level 10 and progress to higher levels with increments based on teaching experience, research output, and administrative responsibilities.

3. Extra Benefits at IITs
- Research Grants: IITs provide seed grants ranging from ₹10-50 lakhs to start research projects.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): 24-30% based on city classification.
- Medical Benefits: Free or highly subsidized medical care for the employee and dependents.
- Travel Grants: International conference funding for presenting papers.
- Retirement Benefits: PF contributions, pension plans, and gratuity.
4. Additional Facilities
- Housing: On-campus housing at highly subsidized rates.
- Child Education Support: Fee reimbursements or subsidized schooling.
- Leave Policy: Sabbaticals for research and flexible leaves for personal reasons.
- Clubs and Amenities: Access to gyms, sports clubs, libraries, and recreational centers.
Assistant Professor Salary in Universities
1. Age, Education, and Eligibility
- Age Limit: The maximum age limit for Assistant Professor positions in universities can be up to 40 years for general category candidates. However, relaxations are available for reserved categories (SC/ST/OBC) and women candidates as per UGC guidelines and government regulations..
- Educational Qualifications:
- Assistant Professor: Master’s degree with 55% marks and NET qualification or Ph.D. as per UGC regulations.
- Important Note: Candidates with a Ph.D. obtained from universities ranked in the top 500 globally (as per QS/Times Higher Education rankings) are exempted from NET/SLET/SET.
- Associate Professor: Ph.D. with 8 years of experience, 7 publications, and a minimum research score of 75.
- Professor: Ph.D. with 10 years of teaching or research experience and 10 publications, with a total research score of 120.
2. Salary Structure
Universities also follow the UGC 7th Pay Commission framework:
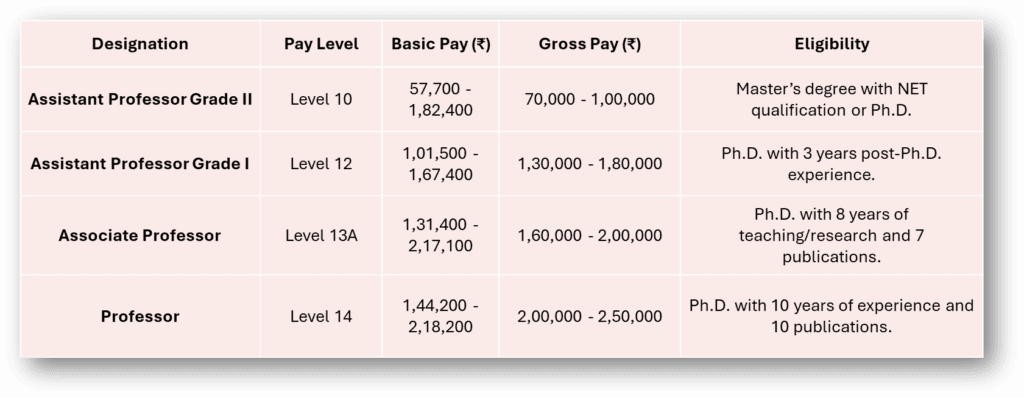
3. Extra Benefits at Universities
- Dearness Allowance (DA): 50% of the basic salary.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): 8-30% based on the city.
- Medical Insurance: Comprehensive healthcare for employees and dependents.
- Leave Benefits: Maternity and paternity leave, earned leave, and research leaves.
4. Additional Facilities
- Campus Housing: Provided at nominal rents, especially in government universities.
- Research Grants: Funds for conference participation and small-scale research projects.
- Library and Labs: Access to university facilities for research purposes.
- Travel Allowances: Partial reimbursement for travel related to academic duties.
IIT vs University – A Comparison
1. Salary
- IITs: Salaries at IITs are higher, ranging from ₹70,900 to ₹2,50,000, depending on qualifications, experience, and seniority. IITs offer structured pay scales and competitive increments based on performance and research output.
- Universities: Salaries in universities are also competitive, ranging from ₹57,700 to ₹2,50,000. However, increments and pay progression often depend on tenure and academic scores as per UGC norms.
2. Benefits
- IITs:
- Larger research grants ranging from ₹10-50 lakhs for starting projects.
- Housing facilities are often provided within the campus at subsidized rates.
- Higher House Rent Allowance (HRA), up to 30%, for those living off-campus.
- Travel grants for attending international conferences and research collaborations.
- Better medical benefits, including coverage for dependents.
- Flexible leave policies, including sabbaticals for research and academic purposes.
- Universities:
- Dearness Allowance (DA) at 50% of basic pay.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA) ranges between 8% and 30%, depending on city classification.
- Medical insurance and maternity/paternity leave benefits.
- Research grants for minor projects and conference participation.
- Access to libraries and labs for research purposes.
3. Growth Opportunities
- IITs:
- Rapid career progression based on research achievements, patents, and publications.
- Frequent promotions for high-performing faculty based on research output rather than seniority.
- Opportunities for international collaborations and visiting scholar programs abroad.
- Access to interdisciplinary and cutting-edge research infrastructure.
- Universities:
- Career growth depends heavily on tenure, teaching experience, and academic performance.
- Promotions may take longer and are often influenced by administrative requirements.
- Focus is more on teaching excellence rather than research output.
- Limited international exposure compared to IITs, but opportunities for regional impact.
4. Work-Life Balance
- IITs: Flexible schedules, lower teaching loads, and more focus on research allow for better work-life balance. Faculty members often split their time between research and teaching.
- Universities: Teaching loads are generally higher, leaving less time for research activities. However, the structured academic calendar ensures predictability in schedules, which may be ideal for those focused more on teaching than research.
5. Recognition and Prestige
- IITs: Being part of IIT faculty is often considered more prestigious due to their international reputation, advanced research facilities, and alumni success stories.
- Universities: Universities play a crucial role in democratizing education and impacting regional development. While they may not have the same global recognition as IITs, they are highly respected institutions at the national level.
Final Note:
The role of an Assistant Professor in India provides a prestigious entry into academia, whether in IITs or universities. While IITs offer better salaries, faster growth, and advanced facilities, universities are ideal for candidates focused on teaching and contributing to regional development. Both environments cater to different aspirations, making them equally attractive based on personal preferences and goals.
Regardless of the institution, the 7th Pay Commission ensures competitive salaries and benefits, reinforcing the importance of higher education and research in India. Data referenced from IIT Gandhinagar, IIT Jodhpur, and JNU official sources.
For more amazing knowledge and insights, stay tuned to BioCareersHub!

1 thought on “Assistant Professor Salary in India”